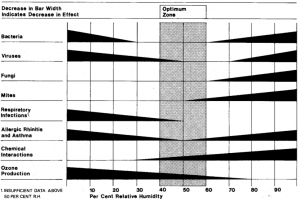
In addition to the energy performance and durability of the building envelope, one of the most significant factors within the indoor environment is the relative humidity of the air (RH), which influences the comfort of occupants and the indoor air quality (IAQ). A steady indoor environment, with a small range of temperature and RH variation will provide the most comfortable climate for its occupants. The optimum levels of RH are between 40% and 60% (figure 1), with levels outside of this optimum range associated with discomfort, health risks and degradation of a building. RH levels above 60% can lead to condensation within a building, resulting in the growth of microorganisms and chemical reactions. RH levels below 40% are associated with discomfort and respiratory conditions. (Fang et al., 1998, Toftum, 1998, Lucas, 2002).
- Optimum relative humidity range for minimising adverse health effects (Sterling, 1986)


Speak Your Mind
You must be logged in to post a comment.